Tunneling (2)
II]
TUNNELLING TROUGH IN DECCAN TRAP BASALT (OR IN COMPACT BASALT OR IN AMYGDALOIDAL BASALT OR IN A JOINTED ROCK)
1) Joints are also
natural divisional planes in the rocks. It is main source of trouble during
tunneling.
2) Because of
fragmentation it leads to roof falls, also passage way for ground water.
4) Hard rocks are
suitable for tunneling point of view but it is necessary to determine nature
and spacing of natural divisional planes like joints in them.
5) Rock with closely
spaced, open, regular and consistent. Joints or thin bedded rocks will be more
troublesome than those with broadly spaced, irregular and inconsistent
jointing.
6) In case of
horizontal bed or lava flows the condition are ideal if there is a soft bed
underlain and hard bed overlaid. Tunnel should be cut in the soft rock
formation so that hard bed is act as floor and ceiling of floor.
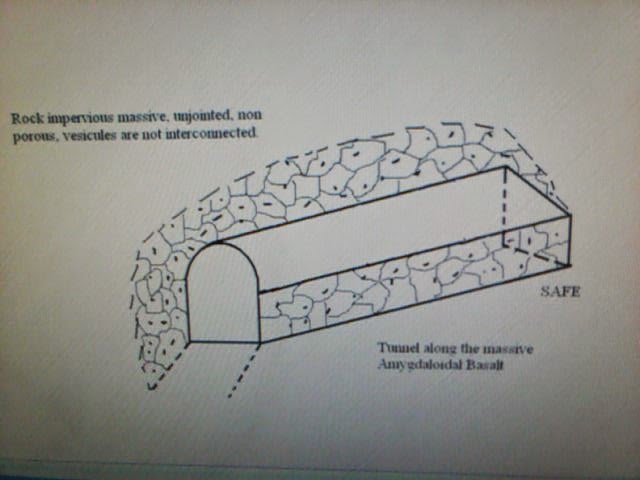
7) In Deccan trap area
two main types of basalt occure a) compact basalt b) Amygdaloidal basalt. These
two basalt are different in jointing. The compact basalt are well jointed where
as Amygdaloidal basalt are unjointed.
8) Tunnel in compact
basalt often very difficult. While the Amygdaloidal basalt very high rank
suitable for tunneling, because of it is unjointed. They allow excavation to
design section without overbreak, are stable, also completely impervious.
9) Examples :- i) A
large part of Koyna 3rd stage tail race tunnel has been excavated
through a closely jointed . Compact basalt, constant roof fall, heavy
overbreakes and leakage of water through joints tunneling very difficult and
expensive.
ii) Bassein creck tunnel carry the
water from vaiterna river to Bombey city. In this tunnel there is also
tremendous inflow of water through jointed compact basalt.
Tunnel excavated through
amygdaloidal basalt all without any trouble, all of them are totally dry
inspite of being in heavy rain fall areas.
i) Head race tunnel of
Koyna Hydro electric project 3rd stage.
ii)
3rd line in Thal Ghat on Bombey –Delhi line.
iii) Bor Ghat on the
Bombey – Puna line of central railway line about 20 tunnels are through
amygdaloidal basalt.
Totally different behaviour of two
varieties of same rock type basalt in tunneling because of the difference in
jointing.


0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home